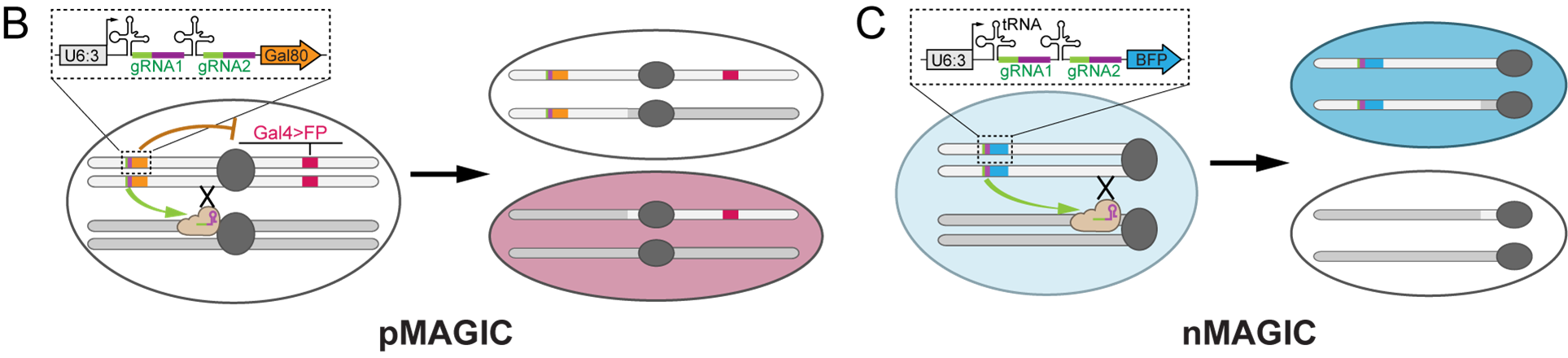
A CRISPR/Cas9-induced double-strand break at a defined chromosomal location at G2 phase causes somatic recombination, generating homozygous twin-spot daughter cells. The MAGIC technique utilizes a gRNA-marker transgene to induce crossover near the centromere and to label the marker-negative homozygous clones. GAL80 is the marker in pMAGIC to enable positive labeling of the clones by GAL4-driven fluorescent protein (FP) expression. In nMAGIC, the clones are negatively visualized by the absence of the BFP marker.

This method is published in Allen et al., 2021: Versatile CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mosaic analysis by gRNA-induced crossing-over for unmodified genomes PLoS Biol. 19(1):e3001061. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001061

