In the split-GAL4 system, restriction of UAS expression is accomplished by expressing the GAL4 DNA-binding domain fused to the Zip- protein-pairing domain in one pattern and a transcriptional activation domain fused to the Zip+ protein-pairing domain in another pattern resulting in expression from a UAS reporter only in the intersection of the two patterns.
As also shown below, this system can be extended to reflect three expression patterns by including a construct expressing a protein that competes for Zip- binding. This "Killer Zipper" protein, consisting of the GAL4 DNA-binding domain fused to the Zip+ protein-pairing domain, can be expressed directly under control of cell-specific regulatory sequences or indirectly under LexAop control.
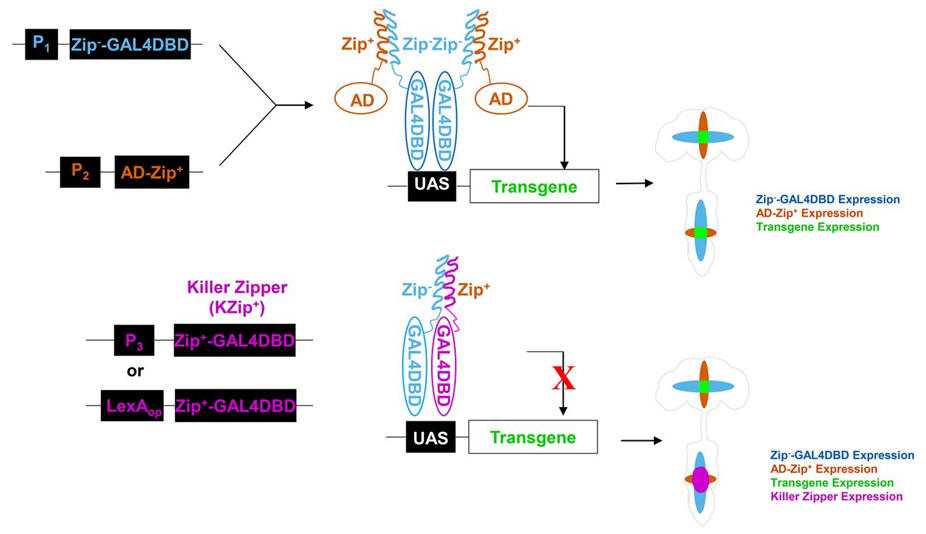
An example is shown below of Killer Zipper expression eliminating split-GAL4 activation of UAS-Venus expression in the nerve cord, but not the brain lobes.
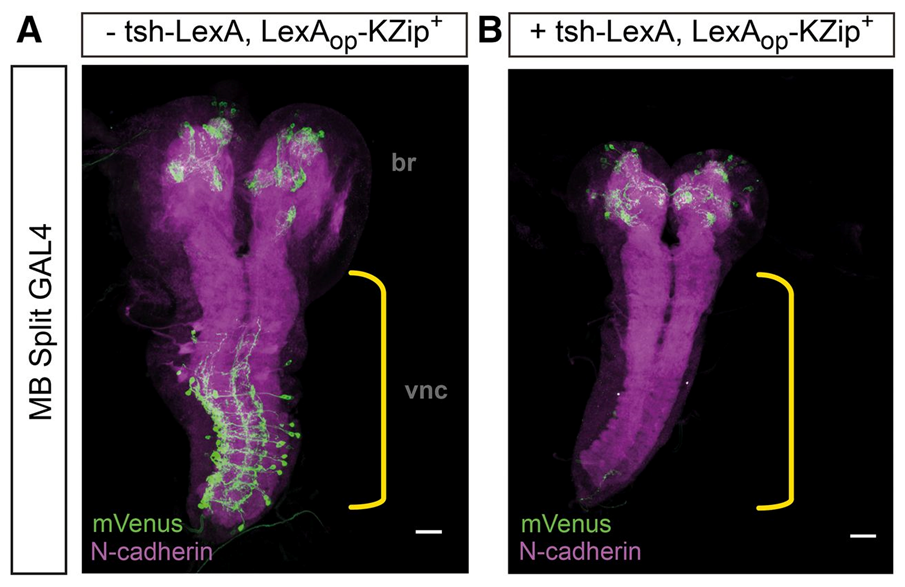
This method was described in Dolan et al. (2017). Facilitating Neuron-Specific Genetic Manipulations in Drosophila melanogaster Using a Split GAL4 Repressor. Genetics 206: 775--784.

